Contributions
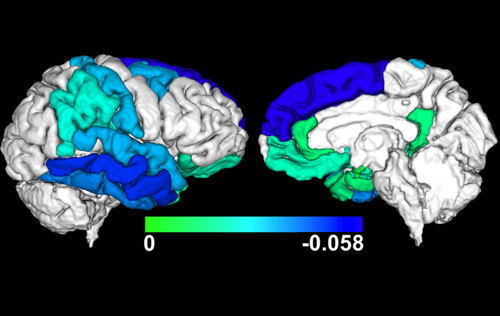
- We have mapped the effects of Alzheimer's pathology and hippocampal sclerosis on the shape of the hippocampus, and demonstrated for the first time that hippocampal atrophy is more substantial in hippocampal sclerosis than Alzheimer's.
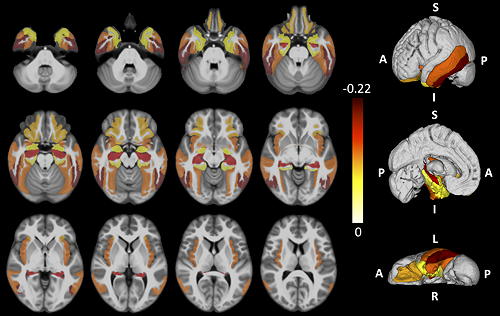
- We have generated the signatures of Alzheimer's and hippocampal sclerosis on regional brain volumes, and showed for the first time that hippocampal sclerosis is associated with atrophy not only in temporal lobe regions in the vicinity of the hippocampus, but also in frontal lobe regions with strong connections to the hippocampus.
- We have shown that regional volumes in the temporal lobe, as well as T2 values in temporal and frontal lobe regions explain a substantial portion of the variance in cognition above and beyond what is explained by demographics and neuropathologies.
- We have generated the signatures of Alzheimer's pathology, hippocampal sclerosis and gross infarcts on T2 constants.
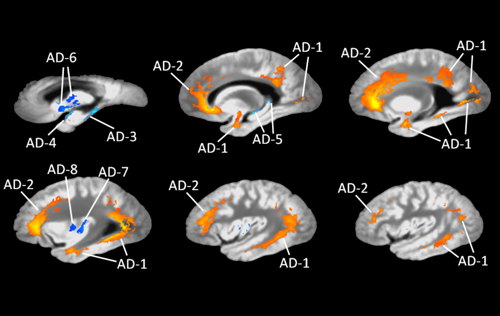
- We have generated for the first time the signature of limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy neuropathologic change (LATE-NC) on regional brain volumes.
- We have shown that white matter hyperintensities are associated not only with vascular pathologies, but also with Alzheimer's pathology.
- We have shown that enlarged perivascular spaces are associated with infarcts, cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA) and diabetes independent of other age-related neuropathologies.
- We have demonstrated that cerebral microbleeds in the frontal lobe are associated with CAA and arteriolosclerosis.
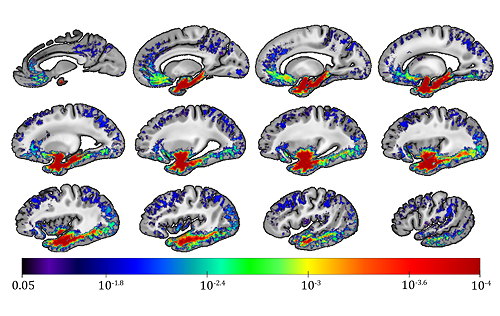
- We have presented for the first time the signature of LATE-NC on brain transverse relaxation rate (R2), and the effects of LATE-NC on white matter structural integrity and connectivity.
- We have mapped the effects of various age-related neuropathologies on the volume and shape of deep gray matter structures.
- We have mapped for the first time the effects of CAA on R2.
The combination of ex-vivo MRI and neuropathology of human brain tissue can enhance investigation of the neuropathological correlates of brain abnormalities and assist in the development of biomarkers of various age-related neuropathologies. Ex-vivo MRI provides images at essentially the same time as histological examination of the tissue, ensuring that no additional pathology develops between imaging and histology. Furthermore, ex-vivo MRI allows imaging independent of frailty level. We have developed a unique large, longitudinal, clinical, pathologic, ex-vivo MRI database including data from community-dwelling older adults. Through these studies we have revealed novel MRI signatures of various age-related neuropathologies.
Selected Related Publications
- Dawe RJ, Bennett DA, Schneider JA, Arfanakis K. Neuropathologic correlates of hippocampal atrophy in the elderly: a clinical, pathologic, postmortem MRI study. PLoS One 2011;6:e26286.
- Dawe RJ, Bennett DA, Schneider JA, Leurgans SE, Kotrotsou A, Boyle PA, Arfanakis K. Ex vivo T2 relaxation: associations with age-related neuropathology and cognition. Neurobiol Aging 2014;35:1549-1561.
- Kotrotsou A, Schneider JA, Bennett DA, Leurgans SE, Dawe RJ, Boyle PA, Golak T, Arfanakis K. Neuropathologic correlates of regional brain volumes in a community cohort of older adults. Neurobiol Aging 2015;36:2798-2805.
- Nelson PT, Dickson DW, Trojanowski JQ, Jack CR, Boyle PA, Arfanakis K, Rademakers R, Alafuzoff I, Attems J, Brayne C, Coyle-Gilchrist ITS, Chui HC, Fardo DW, Flanagan ME, Halliday G, Hokkanen SRK, Hunter S, Jicha GA, Katsumata Y, Kawas CH, Keene CD, Kovacs GG, Kukull WA, Levey AI, Makkinejad N, Montine TJ, Murayama S, Murray ME, Nag S, Rissman RA, Seeley WW, Sperling RA, White Iii CL, Yu L, Schneider JA. Limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy (LATE): consensus working group report. Brain. 2019;142:1503-1527.
- Makkinejad N, Schneider JA, Yu J, Leurgans SE, Kotrotsou A, Evia AM, Bennett DA, Arfanakis K. Associations of amygdala volume and shape with transactive response DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43) pathology in a community cohort of older adults. Neurobiol Aging. 2019;77:104-111.
- Arfanakis K, Evia AM, Leurgans SE, Cardoso LFC, Kulkarni A, Alqam N, Lopes LF, Vieira D, Bennett DA, Schneider JA. Neuropathologic Correlates of White Matter Hyperintensities in a Community-Based Cohort of Older Adults. J Alzheimers Dis. 2020;73:333-345.
- Tazwar M, Evia AM, Tamhane AA, Ridwan AR, Leurgans SE, Bennett DA, Schneider JA, Arfanakis K. Limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy neuropathological change (LATE-NC) is associated with lower R2 relaxation rate: an ex-vivo MRI and pathology investigation. Neurobiol Aging. 2022;117:128-138.
- Nikseresht G, Evia AM, Nag S, Leurgans SE, Capuano AW, Agam G, Barnes LL, Bennett DA, Schneider JA, Arfanakis K. Neuropathologic correlates of cerebral microbleeds in community-based older adults. Neurobiol Aging. 2023;129:89-98.
- Javierre-Petit C, Kontzialis M, Leurgans SE, Bennett DA, Schneider JA, Arfanakis K. Quantitative assessment of enlarged perivascular spaces via deep-learning in community-based older adults reveals independent associations with vascular neuropathologies, vascular risk factors and cognition. Brain Commun. 2024;6:fcae252.
- Tazwar M, Evia AM, Ridwan AR, Leurgans SE, Bennett DA, Schneider JA, Arfanakis K. Limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy neuropathological change (LATE-NC) is associated with abnormalities in white matter structural integrity and connectivity: An ex-vivo diffusion MRI and pathology investigation. Neurobiol Aging. 2024;140:81-92.
- Saifullah K, Makkinejad N, Yasar MT, Evia AM, Leurgans SE, Bennett DA, Schneider JA, Arfanakis K. Neuropathological Correlates of Volume and Shape of Deep Gray Matter Structures in Community-Based Older Adults. Hum Brain Mapp. 2025;46:e70273.
- Yasar MT, Evia AM, Tazwar M, Leurgans SE, Bennett DA, Schneider JA, Arfanakis K. Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy Is Associated With Higher R2 Relaxation Rate: An MRI and Pathology Study. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2025;12:1214-1224.